


Busy supporting customers? Not anymore.
Watch hands-on webinar on workflows and easily automate your work in just five minutes!
Customer self-service solutions are revolutionizing support dynamics. These options empower your recipients and make assistance operations way more efficient.
In this guide, I’ll discuss the positive impact of self-service on both customers and your support reps. See how it revolutionizes customer service, freeing agents to handle more complex tasks. Let’s dive right in!

Self-service refers to a convenient system or approach that enables individuals to perform tasks or access information without the assistance of employees or service providers. It empowers users by giving them direct control over their activities through technology-based interfaces or automated processes.
In practice, customer self-service can take different forms depending on the context. For example, retail can include self-selecting and buying products from shelves or using self-service stations. In banking, self-service options include online banking, ATMs, or mobile banking apps that allow customers to conduct transactions without visiting a physical branch. The use cases don’t end there though.
The advantages of self-service are numerous! They’re easily accessible and increase efficiency, reduce waiting times, provide convenience, and lead to higher satisfaction. By incorporating a self-service strategy and allowing individuals to access resources independently, you can streamline processes, save time, and offer a more personalized experience. You can also unburden employees from routine and repetitive tasks, letting them focus on more complex or valuable activities.
Keep in mind that customer self-service isn’t suitable for all tasks or services. Some situations may still require human assistance or intervention, especially for more specialized needs.
From ordering food to managing finances, self-service solutions streamline operations, provide convenience, and reshape users’ engagement with products and services.
Let’s examine the types and benefits of customer self-service options, their use in various industries, and the changes they bring.
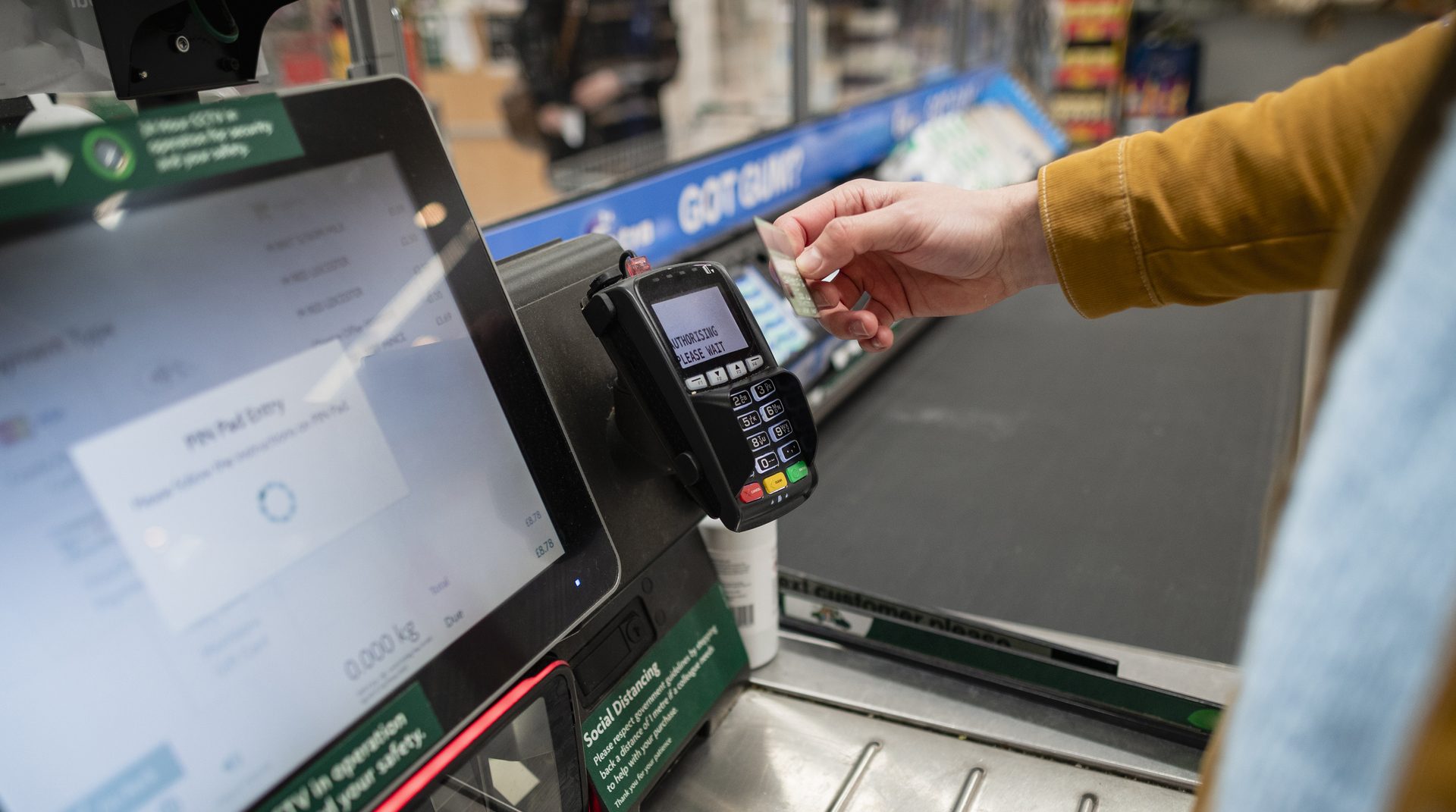
Self-checkout systems are automated stations in retail stores that allow customers to scan and pay for their items independently. These solutions provide a convenient and time-saving alternative to traditional cashier-assisted transactions. Users can locate the barcode on each item, scan it using a handheld scanner or a built-in scanner on the station, and then place the items in a bagging area.
 Source: nerdwallet.com
Source: nerdwallet.com
Then, the system calculates the total cost, and customers can complete the payment process by inserting cash, swiping a credit or debit card, or using mobile payment options such as Apple Pay or Google Pay. Self-checkout solutions often include features like weighing scales for produce, age verification for restricted items, and touchscreens for user interaction.
A help center is a centralized online resource that provides self-service options for recipients to find information, troubleshoot problems, and seek assistance. They typically include a search bar, comprehensive FAQs, troubleshooting guides, product manuals, video tutorials, and knowledge bases that cover common concerns.
 As a result, users can access the help center to find answers to common questions or explore step-by-step instructions at their own pace. If that’s not enough, the help center can also provide live chat or ticketing features to respond to questions on the fly. The agent can identify the article viewed by the user and instruct them based on that.
As a result, users can access the help center to find answers to common questions or explore step-by-step instructions at their own pace. If that’s not enough, the help center can also provide live chat or ticketing features to respond to questions on the fly. The agent can identify the article viewed by the user and instruct them based on that.
HelpDesk experts keep help center articles fresh and user-friendly to make using the ticketing system a breeze. Get the 14-day trial for HelpDesk and use our resources 👌
Kiosks are self-contained computer terminals with touchscreens that provide various services and information to users. They’re commonly found in public spaces like airports, hotels, shopping malls, and healthcare facilities. Users can interact with the kiosk by touching the screen to access different options and functionalities.
Interactive kiosks can offer self-check-in for flights or hotel reservations, interactive maps and directories, ticket purchasing for events or transportation, printing or scanning, access to tourist information, and even language translation services. They’re designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, providing an experience that saves time and improves convenience.
Online and mobile banking have revolutionized how people manage their finances. Banks and financial institutions offer secure online platforms and mobile apps that allow users to access their accounts and perform various banking tasks remotely. With online banking, customers can view their account balances, transaction history, and statements, transfer funds between accounts, pay bills, set up automatic payments, apply for loans or credit cards, manage investments, and even communicate with agents.
Mobile banking extends these functionalities to smartphones and tablets, enabling users to perform banking tasks on the go using dedicated apps. Features like biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition) and real-time notifications enhance security and provide a seamless banking experience.
ATMs are electronic devices allowing bank customers to perform basic banking transactions without visiting a branch or interacting with a teller. These self-service machines are typically available 24/7 and are strategically placed in various locations for easy accessibility.
ATMs provide cash withdrawals, cash or check deposits, balance inquiries, account transfers, bill payments, and purchasing prepaid cards. Customers insert their bank or credit card into the machine to use an ATM and enter their PIN (personal identification number) for security verification. The user interface guides customers through the transaction process, and receipts are usually provided for record-keeping.
Self-service ticketing systems are widely used in the transportation industry to streamline the ticket-purchasing process for passengers. These systems allow travelers to purchase tickets and choose their seats using various channels. Online platforms and mobile apps enable customers to browse schedules, select routes, view seat availability, and make secure payments electronically.
Ticket vending machines are often located at transportation stations or terminals, providing a self-service option for those who prefer to purchase tickets in person. These machines feature touchscreens or button interfaces for navigating through ticket options and payment methods. This solution saves customers time, reduces queues, and improves operational efficiency for transportation providers.
Customer self-service gas stations offer a convenient option for customers to refuel their vehicles without needing an attendant. Users can select a fuel pump, insert their credit or debit card, or pay with a mobile payment option to authorize the fueling process. They can then fill their vehicles with the desired amount of fuel, monitor the transaction on the pump display, and receive a receipt upon completion.
A customer self-service portal is an online platform companies provide to offer self-service support options for their customers. These portals serve as a centralized hub where users can access various resources and tools to find solutions to their queries.
 Source: dunnsolutions.com
Source: dunnsolutions.com
In addition, customer service portals often incorporate live chat support or email handling features, allowing users to communicate directly with support representatives when needed.
Did you know that HelpDesk provides 24/7 support? You can contact us for any issue at any time. Get the HelpDesk 14-day trial and try us out! 😎
Self-service restaurants are establishments where customers can independently place their orders, make customizations, and collect their food without the assistance of waitstaff. These restaurants often employ the customer self-service system through kiosks or mobile apps, which allow users to browse menus, select items, specify preferences (such as toppings or condiments), and complete the payment process.
 Source: info.restaurantspacesevent.com
Source: info.restaurantspacesevent.com
Some self-service restaurants utilize table sensors or number-based systems to track orders, enabling staff members to deliver the food to the correct table. By offering self-service options, restaurants can improve efficiency, reduce wait times, and provide a more personalized dining experience.
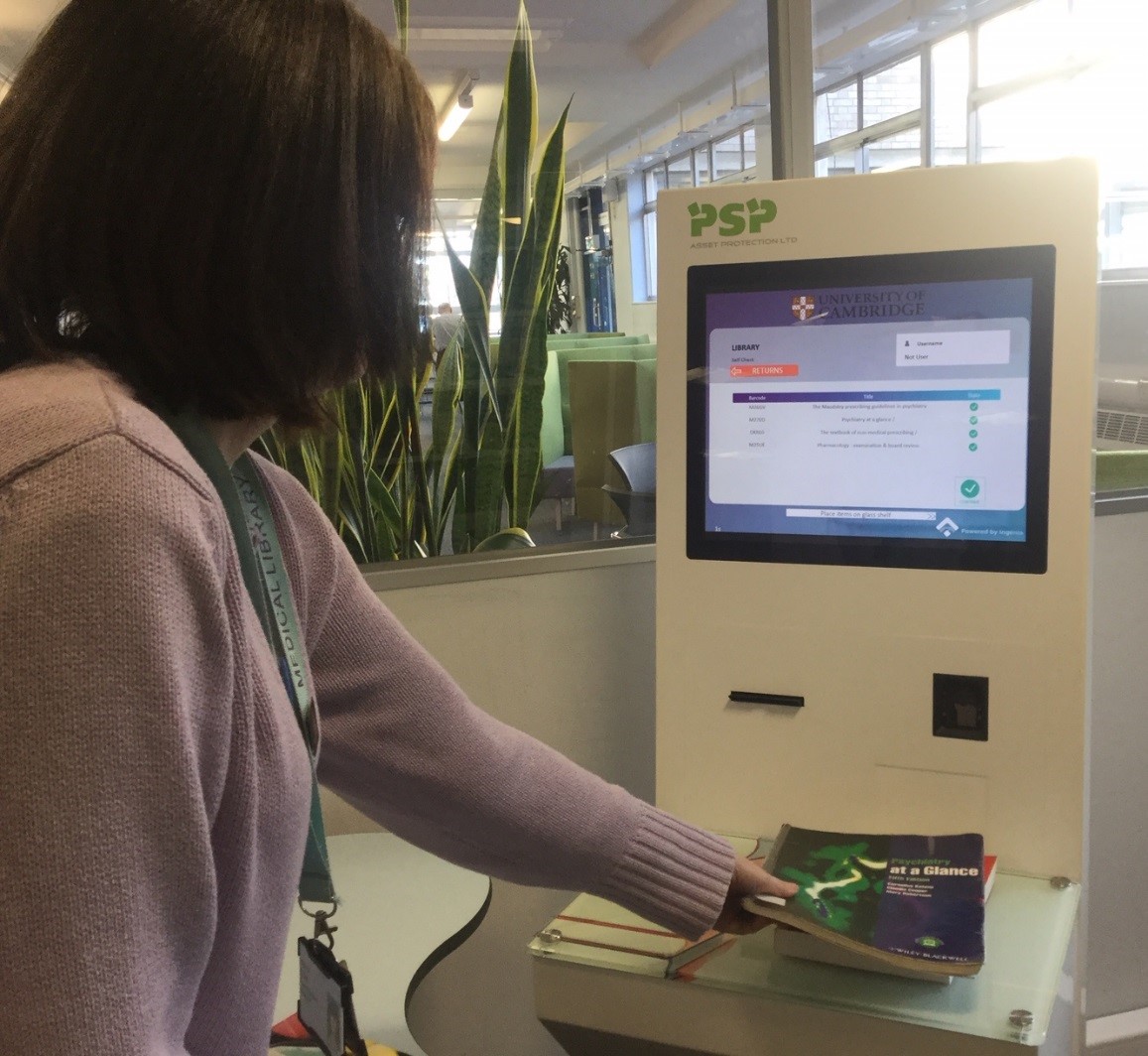
Library self-checkout machines provide patrons with a convenient way to borrow and return books, CDs, and other materials without requiring assistance from library staff. These machines are equipped with scanners or barcode readers, allowing users to scan their library cards and the barcodes on the items they wish to borrow or return. The system verifies the transaction, updates the user’s account, and prints a receipt if needed.
 Source: hongzhousmart.com
Source: hongzhousmart.com
Also, library self-checkouts often feature user-friendly interfaces that guide patrons through the process and may include additional functionalities like account access for renewals or holds. By implementing self-checkout systems, libraries can streamline their operations and empower users to manage their borrowing activities independently.
Online handbooks or manuals are comprehensive resources that provide detailed information and instructions on using a product, service, or system. These digital documents are accessible to users and can be accessed at any time, allowing individuals to self-educate and troubleshoot issues without the need for human assistance.
 Online handbooks, such as HelpDesk’s one-stop handbook, often include step-by-step guides, diagrams, illustrations, and frequently asked questions to guide users through various processes and provide them with the necessary information to succeed.
Online handbooks, such as HelpDesk’s one-stop handbook, often include step-by-step guides, diagrams, illustrations, and frequently asked questions to guide users through various processes and provide them with the necessary information to succeed.
Explore HelpDesk's one-stop handbook to take full advantage of the free 14-day trial! 🔥
These are just a few examples of self-service options, and the specific implementations can vary depending on the industry and organization. As you can easily see, they all aim to enhance convenience, reduce wait times, and give users greater control over their transactions and interactions.
Self-service options have become valuable as customers increasingly seek convenience, efficiency, and independence in their brand interactions. Self-service platforms are revolutionizing how customers consume products, services, and information, putting the power directly into their hands.
Let’s explore the significant advantages that self-service brings to customers!
Customers can access self-service options anytime and from anywhere, eliminating the constraints of traditional business hours. Whether purchasing products online, accessing frequently asked questions, or resolving simple issues, self-service allows people to engage with the company’s offerings conveniently. This flexibility saves time and effort, allowing customers to complete tasks efficiently and effortlessly.

Recipients can access comprehensive databases, knowledge bases, and FAQs that provide detailed information about products, services, and common topics. This lets them quickly find answers to queries without waiting for a customer service rep. Additionally, a self-service portal often offers troubleshooting guides and step-by-step instructions, enabling customers to resolve issues independently, further reducing the need for assistance.

Self-service options empowercustomers and give them a sense of ownership over their interactions. Instead of relying on a customer service representative, they can independently navigate through the self-service platform, finding the exact information they need and taking appropriate actions. Such empowerment increases satisfaction as people gain autonomy and self-reliance in their efforts.

Many self-service platforms enable the personalization of customer service experience based on the identified choices and previous interactions. Customers can create profiles, set preferences, and receive tailored recommendations, starting a customized journey that aligns with their unique needs.

By enabling customers to find answers on their own, self-service not only empowers them but also lightens the workload for support staff. Through self-service adoption, agents can streamline operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive overall efficiency.
Discover the numerous benefits of self-service to teams, revolutionizing how organizations handle customer cases.
By providing customers with self-service options, your customer service team can significantly reduce their workload and the number of incoming tickets. Customers can access knowledge bases, FAQs, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides to find answers to common queries and resolve simple issues independently. This allows agents to focus on complex cases and critical customer concerns.

Self-service support tools enable support teams to automate repetitive tasks and routine inquiries. Customers can access instant solutions without waiting for support reps by leveraging chatbots, virtual assistants, or interactive FAQ pages. This automation frees up support agents’ time and makes them more productive in delivering timely advice.

Quick access to information increases people’s fulfillment and reduces the frustration of waiting for backup. When customers can solve their own concerns, they feel empowered and gain more trust in the company. This positive experience improves loyalty and increases the likelihood of repeat purchases.

Self-service platforms provide an excellent opportunity for agents to incorporate relevant product recommendations, add-on sales opportunities, and cross-selling. You can give additional offers or complementary products that align with identified customer needs when they seek details. This approach helps agents generate additional revenue streams and maximize the delivered value.

Self-service platforms often come with analytics capabilities, allowing your support representative to gather valuable data about customer behavior, preferences, and commonly encountered issues. By analyzing this data, the support team can identify patterns, pain points, and areas for improvement. These insights enable agents to proactively address customer concerns, refine self-service resources, and optimize their support processes to better serve in the future.

By understanding people’s needs, wielding the right tools and technologies, and embracing continuous improvement, you’re about to create a joyfully seamless experience like never before!
Dive into the essential steps for successful customer self-service implementation, unlocking the benefits of customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Analyze customer support tickets and categorize the most common issues.
Conduct customer surveys to gather feedback on areas where self-service could be beneficial.
Monitor customer interactions on social media and online forums to identify recurring concerns.
Specify measurable goals such as reducing support ticket volume by a certain percentage or improving response times.
Align objectives with broader business objectives, such as cost reduction or customer satisfaction improvement.
Evaluate customer preferences and demographics to determine the most relevant self-service channels.
Consider the nature of your business and the complexity of customer inquiries.
Explore industry best practices and trends to stay up to date with emerging self-service technologies.
Research common customer questions and issues to create a robust collection of articles.
Organize content into logical categories and subcategories for easy navigation.
Use a content management system (CMS) to ensure the knowledge base is easily accessible and searchable.
Regularly review and update the knowledge base to reflect new product features, updates, or customer feedback.
Design a clean, intuitive interface that guides customers to relevant self-service resources.
Ensure responsive design to accommodate various devices, including desktop, mobile, and tablets.
Conduct user testing to gather feedback on the usability and navigation of the interface.
Implement an AI-powered chatbot that can handle basic customer inquiries.
Train the chatbot to understand natural language and provide accurate and relevant responses.
Continuously improve the chatbot’s performance based on customer feedback and interactions.
Launch an online community forum where customers can interact and support each other.
Encourage active participation by acknowledging and rewarding valuable contributions.
Assign community moderators to monitor discussions, maintain a positive environment, and escalate issues as necessary.
Create instructional videos and interactive guides visually demonstrating product usage or issue resolution.
Ensure the videos and guides are concise, well-structured, and easily understandable.
Make the videos and guides available through various channels, such as your website, YouTube, or a dedicated video library.
Highlight self-service channels on your website’s main navigation or prominent sections.
Incorporate self-service links and resources within email communications, order confirmations, and invoices.
Educate customers about the benefits of self-service through blog posts, social media, or dedicated email campaigns.
Monitor customer feedback and support data to identify gaps or areas for improvement in your self-service offerings.
Regularly review and update the knowledge base content to ensure it remains accurate and relevant.
Analyze search data within your self-service channels to identify commonly searched keywords or topics that need further attention.
Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to track the effectiveness of your self-service implementation.
Monitor ticket deflection rate, average resolution time, customer feedback ratings, and customer satisfaction scores.
Utilize analytics tools to gain insights into user behavior, such as popular search queries or frequently accessed articles.
Offer alternative support channels, such as live chat or phone support, for customers who prefer direct assistance.
Ensure a seamless transition between self-service and human-assisted channels by integrating them into a unified support system.
Educate support agents about the self-service resources available to customers.
Provide effective communication and problem-solving training to assist customers who require human intervention.
Foster collaboration between support agents and self-service content creators to share knowledge and enhance overall support quality.
Regularly solicit customer feedback regarding their self-service experience through surveys or feedback forms.
Conduct user testing sessions to gather direct feedback on the usability and effectiveness of self-service channels.
Actively listen to customer feedback and make necessary improvements based on their suggestions and pain points.
By following these detailed steps and sub-steps, you can implement customer self-service effectively and enhance customer satisfaction in your business.
While self-service offers numerous benefits, it also has its fair share of challenges and common pitfalls. Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for organizations to implement a customer self-service strategy successfully.
Let’s explore key challenges and traps in self-service and discuss strategies to overcome them.
One of the main challenges in implementing self-service solutions is finding the right balance between automated assistance and human support. While self-service aims to provide users with quick and efficient solutions, there are instances where customers may require human intervention for tough or unique situations.
Failing to strike the right balance can lead to frustration among users who feel unsupported or abandoned, as well as potential negative impacts on your relationship. That’s why it’s crucial to carefully determine the appropriate level of self-service and make sure that human support is readily available when needed.
Another common challenge in self-service is confirming the accuracy and relevance of the information provided. Self-service platforms rely heavily on knowledge bases, FAQs, and other resources to assist users.
However, if these sources aren’t regularly updated and maintained, they can become outdated and provide incorrect or obsolete information. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction and a decline in trust. To overcome this challenge, establish robust processes for regularly reviewing and updating their self-service resources to deliver accuracy and applicability.
Self-service platforms often involve collecting and storing sensitive and relevant customer data. Addressing security and privacy concerns is crucial to protect user information from unauthorized access or breaches.
It’d be best to implement robust security measures such as encryption, secure authentication protocols, and regular vulnerability assessments to safeguard customer data. In addition, convey clear and transparent privacy policies to users to build trust in the self-service platform.
Introducing a self-service system to users accustomed to traditional support channels can present user adoption and training challenges. Some users may resist change or hesitate to use self-service tools, resulting in low adoption rates.
Additionally, users may require proper training and guidance to navigate the self-service platform effectively. Provide comprehensive training materials, user-friendly interfaces, and proactive communication to overcome these challenges to encourage user adoption. Ongoing support and feedback channels can also help address any usability issues and enhance the user experience.
In conclusion, customer self-service has emerged as a powerful tool that benefits customers and support teams. By empowering users to find solutions at their own convenience, self-service resources not only enhance their overall experience but also save them time and frustration.
Moreover, self-service significantly lightens the load on support teams, allowing them to focus on more challenging and critical issues. By deflecting routine inquiries, self-service systems help support agents optimize productivity, respond to urgent matters promptly, and deliver more personalized assistance.
Beyond these immediate advantages, self-service also encourages continuous learning and improvement. By analyzing the data generated through self-service platforms, you can gain valuable insights into common pain points, identify areas for enhancement, and refine support strategies accordingly.
While it’s crucial to strike the right balance between self-service and human support, it’s clear that self-service solutions positively impact both customers and support teams.
Self-service paves the way for a more streamlined and effective support experience in today’s digital age by fostering independence, efficiency, and happiness. Embracing self-service isn’t just a trend — it’s a strategic investment you can make to stay ahead in a customer-centric marketplace.
Weronika Masternak
Weronika is a product content designer at HelpDesk. She has a deep passion for telling stories to educate and engage her audience. In her free time, she goes mountain hiking, practices yoga, and reads books related to guerrilla marketing, branding, and sociology.
Try HelpDesk for free
For quick and intuitive tickets management