


Busy supporting customers? Not anymore.
Watch hands-on webinar on workflows and easily automate your work in just five minutes!
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a breakthrough technology revolutionizing customer service. By automating repetitive tasks and ensuring efficient and error-free results, RPA streamlines operations and enhances the customer experience.
This guide explores RPA in customer service, covering the benefits, challenges, and best practices for successful implementation. Browse real-world examples and industry insights to comprehensively understand how RPA transforms customer service, boosting operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.

Traditionally, customer support has relied heavily on human agents to handle queries, resolve issues, and provide assistance. However, this manual approach often resulted in delays, inconsistencies, and human errors, leading to customer dissatisfaction and increased business costs. Organizations recognized the need for a more streamlined and efficient system, so they turned to RPA to transform their customer care and business process.
Robotic process automation utilizes automated software, software robots, or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks that human agents previously performed. These bots can be programmed to handle a wide range of activities, including data entry, form processing, order fulfillment, information retrieval, or even complex decision-making processes. By taking over these mundane tasks, RPA allows customer support agents to focus on more complex and value-added activities, such as solving intricate issues, providing personalized assistance, or nurturing customer relationships.
One of the primary benefits of implementing RPA in customer care is its ability to enhance operational efficiency. By automating routine tasks, organizations can significantly reduce response times, minimize errors, and simultaneously handle a higher volume of customer inquiries. With RPA, customers can experience quicker resolutions, improved accuracy, and round-the-clock support, enhancing overall satisfaction and loyalty.
Moreover, RPA brings scalability and flexibility to customer support operations. As businesses grow and customer demands increase, RPA can easily adapt and handle higher workloads without additional hiring or training. The bots can be scaled up or down based on the fluctuating demand, ensuring consistent support and preventing bottlenecks during peak periods.
However, while RPA offers numerous advantages, balancing automation and human intervention is essential. While bots can handle repetitive tasks effectively, they may lack the corresponding empathy, intuition, and problem-solving skills that human agents possess. As a result, an optimal approach involves integrating RPA with human agents, creating a symbiotic relationship where automation complements and empowers human capabilities.
Now, let’s look at how RPA works!
First, the business identifies the tasks or processes suitable for automation using RPA. These tasks are typically repetitive, rule-based, and involve structured data.
RPA bots are created and trained to perform specific tasks. The development process involves defining the automated workflow, configuring the bot’s actions and logic, and integrating it with the necessary apps and systems.
Once the bot is developed, it’s deployed on the target environment where the automation will occur. This could be a desktop computer, a server, or a cloud-based infrastructure.
The RPA bot interacts with applications and systems through their user interfaces, just like a human user. It can log into systems, navigate screens, fill out forms, extract data, and trigger actions.
RPA bots can process and manipulate data. They can extract and enter information from one system into another, perform calculations or validations, update databases, and generate reports.
RPA bots are designed to handle errors and exceptions that may arise during automation. They can detect and respond to error conditions, log errors, and perform recovery actions if necessary.
RPA platforms provide monitoring and control capabilities to manage and track bots’ performance. This includes tracking task execution, generating reports, managing bot schedules, and monitoring overall automation efficiency.
Automation doesn't have to be complicated! 😎 Get ticket automation software that doesn't require coding skills. Sign up to HelpDesk!
RPA operates at the user interface level and doesn’t require significant changes to the underlying systems or infrastructure. RPA technology can work with various applications, including legacy systems, web-based and desktop apps. RPA brings efficiency, accuracy, and scalability to business processes by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and freeing up human workers to focus on higher-value activities.
From handling routine inquiries and processing requests to accelerating response times and improving data accuracy, RPA has emerged as a game-changer, allowing organizations to deliver seamless and efficient support services.
So, what are robotic process automation tools in customer support?
RPA bots can be configured to analyze incoming customer emails, extract relevant information, and generate automated responses for common inquiries. This helps improve response times and provides customers with instant acknowledgments or initial support.
RPA bots can analyze support tickets or inquiries and classify them based on predefined criteria. They can assign appropriate tags, prioritize urgent issues, and route tickets to the relevant support teams or agents, ensuring efficient and accurate ticket handling.
If you want to automate processes and speed up work on tickets, get HelpDesk 🏃💨 Try automated workflows for 14 days for free!
RPA can automate updating customer information or entering data into CRM or ticketing systems. Bots can extract data from different sources, validate and format it, and populate the customer databases, eliminating manual data entry errors and saving time for support agents.
RPA enables self-service options for customers by automating responses to frequently asked questions. Bots can provide step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting guides, or links to relevant resources, empowering customers to find answers on their own and reducing the need for agent intervention.
RPA bots can collect and analyze customer feedback data from various sources, such as surveys or social media. They can aggregate feedback, identify trends, and generate reports, providing valuable insights to improve customer care processes and address recurring issues.
RPA can automate order processing tasks, such as order entry, payment verification, and tracking updates. Bots can integrate with ecommerce platforms, inventory systems, and shipping carriers, providing smooth order management and real-time status updates for customers.
RPA bots can assist in creating and maintaining a knowledge base for customer support. They can extract information from support tickets, identify frequently asked questions, and update the knowledge base with relevant content. This ensures it remains up-to-date and serves as a valuable resource for customers and agents.
RPA tools can validate customer data, such as contact information or account details, against predefined rules or external databases. They can also automatically update customer records with the latest information from different sources, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
RPA tools can collect and consolidate data from multiple sources to generate reports on key customer support metrics, such as response times, ticket volumes, customer satisfaction scores, and agent performance. These reports can help identify trends, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions.
These are just a few examples of how you can utilize RPA in your customer care. you can see, the possibilities are vast, and RPA can be tailored to your specific needs and processes to streamline operations, improve response times, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
The three main types of robotic process automation commonly recognized are attended RPA, unattended RPA, and hybrid RPA. Each type serves different automation needs within an organization.
Attended robotic process automation involves the collaboration between human workers and software bots. In this scenario, the RPA bots work alongside human users to automate tasks that require human intervention or decision-making. The bots assist employees by performing repetitive and time-consuming tasks, providing suggestions, or retrieving information on demand. Attended RPA is typically used when human judgment is crucial and tasks require real-time interaction.
Unattended robotic process automation operates autonomously without direct human supervision. Bots are designed to execute tasks independently, typically batch or scheduled. Bots can log into systems, access, and process data, perform calculations, generate reports, and handle other rule-based tasks without human involvement. Unattended RPA is well-suited for back-office operations or tasks that can be fully automated and do not require immediate human input.
Hybrid robotic process automation combines the features of both attended and unattended RPA. It offers the flexibility to automate tasks requiring human involvement and unattended automation. Hybrid RPA allows for the seamless integration of human and robotic workflows, enabling organizations to automate end-to-end processes involving manual and automated steps. It can be applied in scenarios where certain parts of a business process require human decision-making or interaction while other parts can be automated.
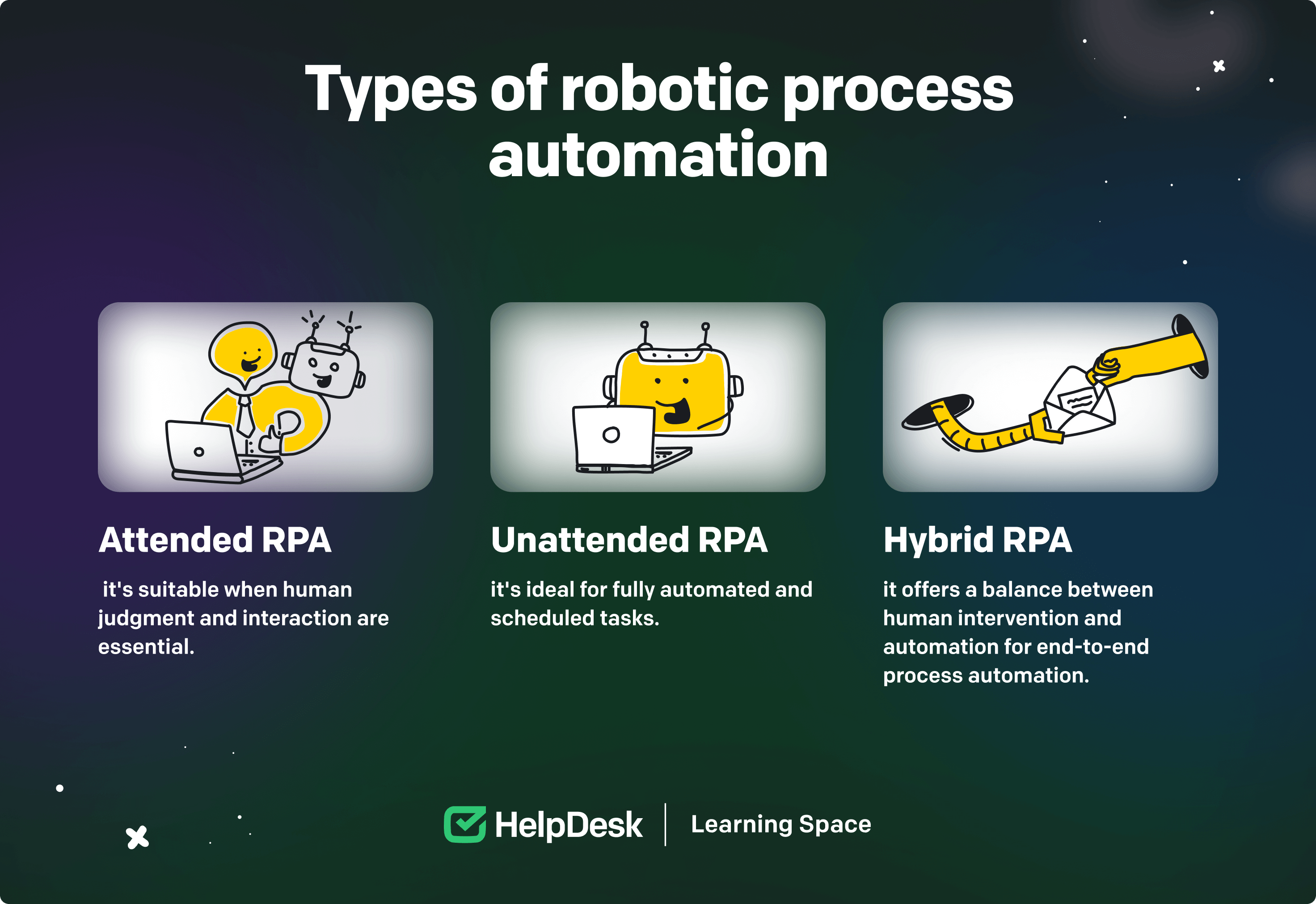 To sum up, attended RPA is suitable when human judgment and interaction are essential, unattended RPA is ideal for fully automated and scheduled tasks, and hybrid RPA offers a balance between human intervention and automation for end-to-end business process automation. Bear in mind that the choice of RPA type depends on your specific automation requirements, the nature of tasks, and the desired level of human involvement.
To sum up, attended RPA is suitable when human judgment and interaction are essential, unattended RPA is ideal for fully automated and scheduled tasks, and hybrid RPA offers a balance between human intervention and automation for end-to-end business process automation. Bear in mind that the choice of RPA type depends on your specific automation requirements, the nature of tasks, and the desired level of human involvement.
RPA and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are both technologies used in automation, but they serve different purposes and have different capabilities.
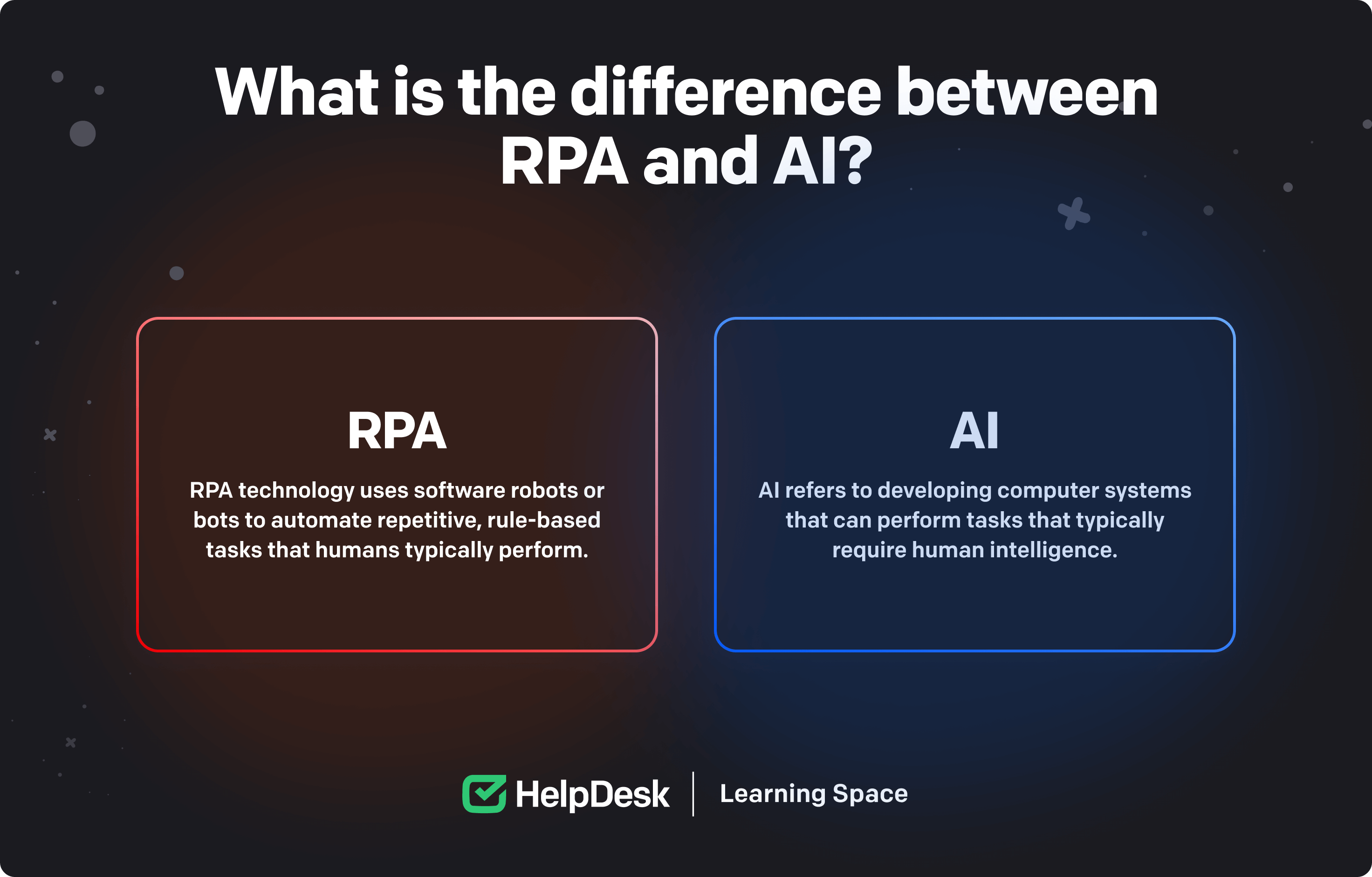
RPA technology uses software robots or bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that humans typically perform.
RPA tools and bots interact with applications and systems just like humans, following predefined rules and instructions. RPA mainly focuses on automating manual, routine tasks, such as data entry, form filling, and screen scraping. It’s designed to mimic human actions and doesn’t possess cognitive abilities.
AI refers to developing computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
AI systems can analyze and interpret data, learn from patterns, make decisions, and even simulate human-like behavior. Unlike RPA, AI doesn’t rely on predefined rules but on algorithms and models that enable machines to learn and improve over time. AI encompasses various subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and deep learning.
In summary, the main differences between RPA and AI are:
Scope. RPA focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, while AI aims to simulate human intelligence and perform complex tasks.
Cognitive abilities. RPA doesn’t possess cognitive abilities and relies on predefined rules, whereas AI systems can learn, adapt, and make decisions based on data and patterns.
Flexibility. RPA is best suited for structured processes that have clear rules and require interaction with existing systems, while AI can handle unstructured data and tasks that require analysis, interpretation, and decision-making.
Complexity. RPA is relatively simpler to implement compared to AI, as it doesn’t require advanced algorithms or models. AI systems often involve more sophisticated algorithms and require substantial training data and computational resources.
In practice, RPA and AI complement each other in automation projects. RPA can handle many of your repetitive tasks, while AI can analyze data, extract insights, and make intelligent decisions you can follow.
Choosing the best software for robotic process automation in customer assistance depends on specific requirements, budget, and the organization’s preferences. Several reputable RPA software providers offer robust capabilities for customer support automation.
UiPath is one of the leading RPA software providers with a strong presence in customer support automation. It offers a user-friendly interface, extensive automation capabilities, and a rich ecosystem of pre-built automation components. UiPath provides features like data extraction, ticket routing, email automation, and integration with various customer support systems.
Automation Anywhere is another well-known RPA software that offers comprehensive solutions for customer care automation. It provides a range of features such as data entry, ticket management, content generation, and integration with CRM systems. Automation Anywhere also offers intelligent automation capabilities through its cognitive automation tool, IQ Bot.
Blue Prism is recognized for its enterprise-grade RPA platform that includes features suitable for customer support automation. It offers visual process automation, ticket management, data validation, and integration with customer support applications. Blue Prism emphasizes security and compliance, making it a preferred choice for organizations with strict regulatory requirements.
Pega Systems provides a comprehensive platform for customer service automation, including RPA capabilities. Their software combines RPA with AI and case management functionalities, allowing for intelligent customer care automation. Pega Systems offers features such as ticket management, knowledge base integration, and personalized customer interactions.
WorkFusion is known for its AI-powered RPA platform that can be applied to various customer care tasks. It offers ticket routing, email processing, data extraction, and workflow automation features. WorkFusion focuses on intelligent automation, enabling organizations to leverage machine learning and cognitive capabilities for customer support optimization.
HelpDesk is a support hub software that offers automation capabilities to streamline support processes. While not solely focused on RPA, HelpDesk provides features such as ticket management, automated ticket routing, canned responses, and multiple integrations.
This software automates repetitive customer support tasks and provides a centralized platform for efficient ticketing operations. HelpDesk’s automations offer functionalities to automate ticket creation, categorization, and assignment based on predefined conditions and actions.
It’s important to evaluate these software options based on your specific needs, scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, and vendor customer care. Additionally, consider factors such as pricing models, licensing, and the availability of community support or training resources. Conducting a thorough assessment and engaging in proof-of-concept trials can help determine the best fit for your organization’s customer support automation requirements.
In conclusion, the advent of RPA has revolutionized the customer care cape, empowering businesses with intelligent process automation capabilities. Robotic process automation technology has emerged as a catalyst, seamlessly integrating with existing systems and streamlining recurring tasks.
By automating manual processes and augmenting human efforts, RPA implementations have paved the way for enhanced operational efficiency and improved customer experiences. The convergence of RPA and business process management has further amplified the benefits, allowing organizations to orchestrate complex workflows and achieve greater agility.
As businesses continue to embrace the power of RPA, it’s evident that this transformative technology will remain at the forefront of customer support, driving innovation and propelling businesses toward a more efficient and customer-centric future.
Weronika Masternak
Weronika is a product content designer at HelpDesk. She has a deep passion for telling stories to educate and engage her audience. In her free time, she goes mountain hiking, practices yoga, and reads books related to guerrilla marketing, branding, and sociology.
Try HelpDesk for free
For quick and intuitive tickets management